Git on Quest#
Git is an open source, distributed version control system that is commonly used for collaboration on code or documents. While it is often used with a hosting service like GitHub, Git can be used locally to track changes within a single repository stored on disk.
Making Git Available#
Git is available as part of the operating system, but that version of Git is old. It is strongly recommended that you load a newer version of Git with the git module before using Git:
$ module load git/2.37.2
Setting up Git#
Before you use Git for the first time on Quest, you need to set the user name and email address it will use when it records your commits. Use the following commands to set this information:
$ git config --global user.name "John Doe"
$ git config --global user.email johndoe@northwestern.edu
You only need to do this one time. Git will remember your name and email.
To view your Git settings, at any time you can run this command:
$ git config --list
Repositories#
You can create repositories at any time in any directory on Quest you
have write access to with the git init command. However, if you wish
to clone a repository from a remote server such as GitHub or Bitbucket,
you have a choice of using either HTTPS or SSH to clone.
Tip
For public, read-only repository, we recommend cloning via HTTPS. For private repositories or when using Git for active development, we recommend cloning via SSH.
Cloning from GitHub with SSH#
To clone a repository from GitHub on Quest using the SSH protocol, you must first load your SSH key from Quest into GitHub. To do this,
Print your public SSH key to screen via the following:
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. This will display several lines of text. Copy it to your computer’s clipboard.Go to GitHub and click your profile in the upper right corner, then click “Settings”:
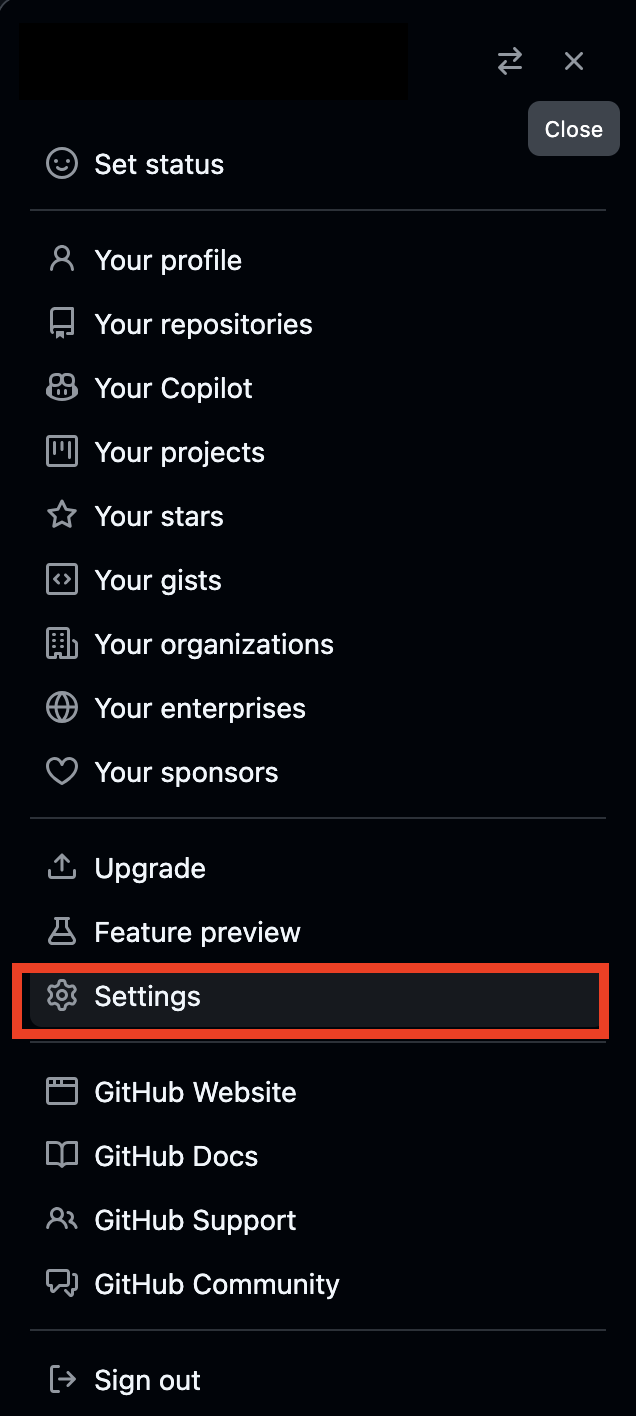
In the left sidebar, click “SSH and GPG Keys”
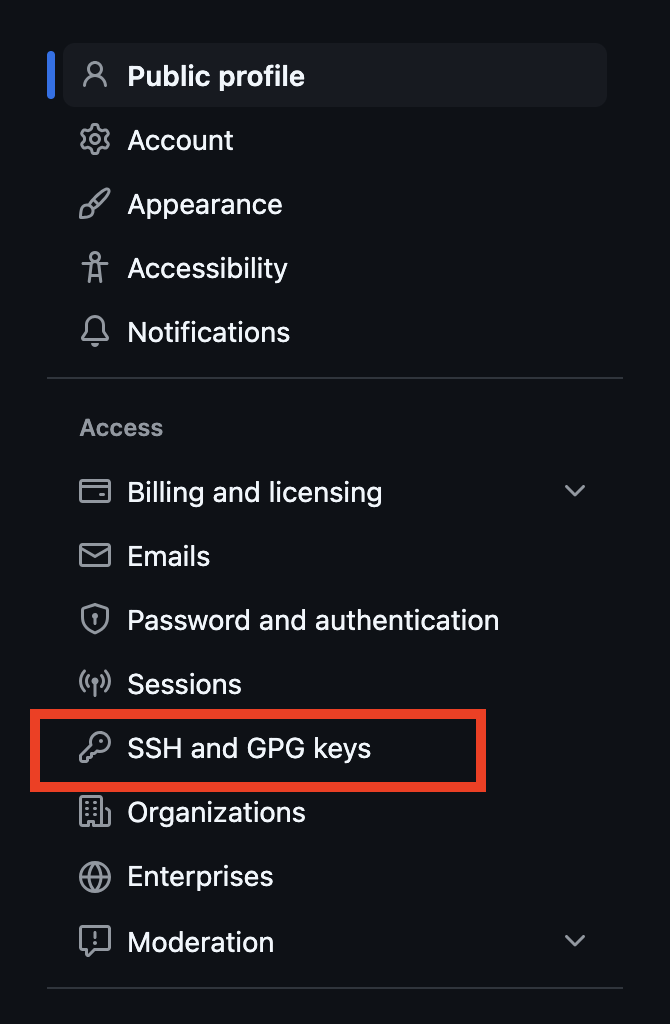
Click “New SSH Key”
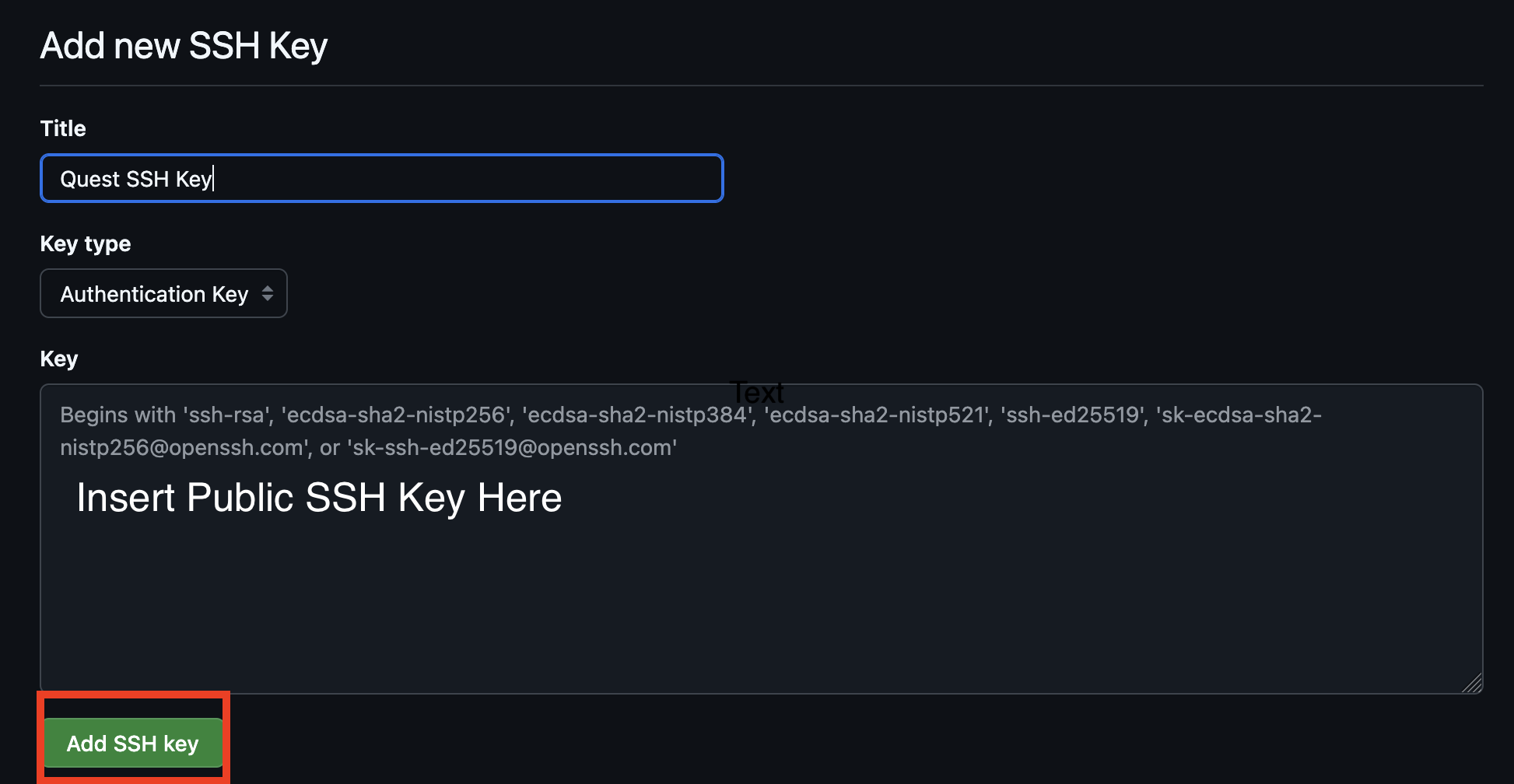
In the “Title” field, enter a descriptive name for the key, such as “Quest SSH Key”. Paste the public key you copied earlier into the “Key” field, then click the “Add SSH Key” button. If prompted, confirm your GitHub password.
Now you are able to clone using the SSH protocol.
To clone a repository using the SSH protocol:
Navigate to the repository (e.g. google-deepmind/alphafold3 )
Click the green “Clone” button
Select the “SSH” tab.
Next, copy the repository URL.
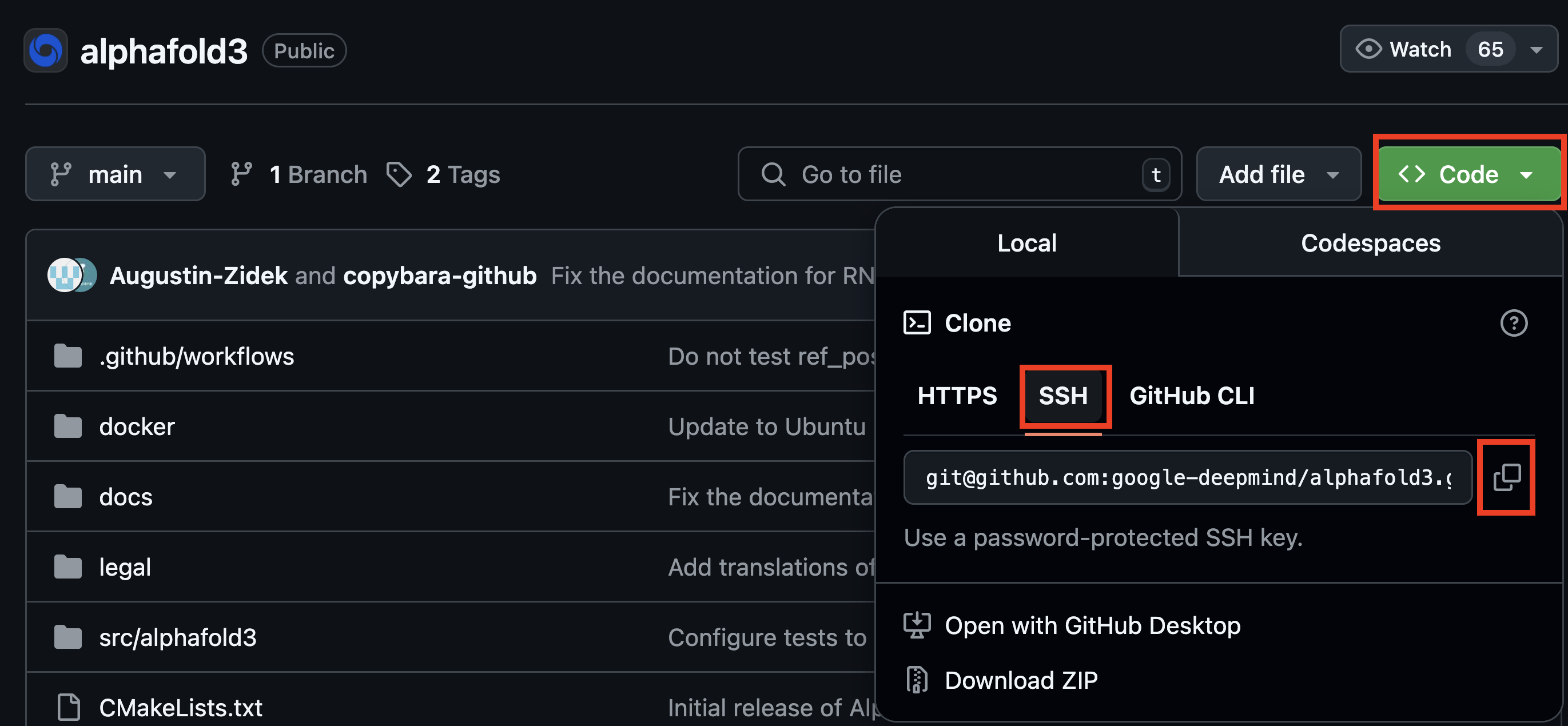
Finally, in your Quest terminal, run this command (pasting in the URL you copied):
$ git clone git@github.com/<organization>/<repository>.git
That will download the repository from GitHub into a directory with the same name as the repository. You will now be able to push and pull from this remote repository without having to enter a username and password.
Git Resources#
There are many tutorials for learning Git on the web. See the Git Resource Guide for a list of resources.
